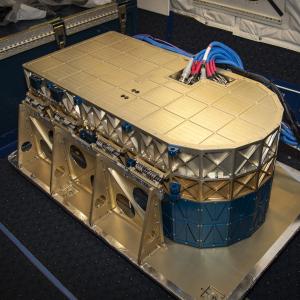
High Altitude Lidar Observatory (HALO)
The NASA Langley High Altitude Lidar Observatory (HALO) is used to characterize distributions of greenhouse gasses, and clouds and small particles in the atmosphere, called aerosols. From an airborne platform, the HALO instrument provides nadir-viewing profiles of water vapor, methane columns, and profiles of aerosol and cloud optical properties, which are used to study aerosol impacts on radiation, clouds, air quality, and methane emissions. When the water vapor, aerosol and cloud products are combined it provides one of the most comprehensive data sets available to study aerosol cloud interactions. HALO is also configured to provide in the future measurements of the near-surface ocean, including depth-resolved subsurface backscatter and attenuation.
- LISTOS (B200 - LARC)
- ACT-America (C-130- WFF)
- Aeolus Cal/Val (DC-8- AFRC)
- CPEX-AW 2021 (DC-8- AFRC)
- CPEX-CV (DC-8 - AFRC)
- STAQS (Gulfstream III - LaRC)
- ecoDemonstrator (DC-8 - AFRC)
- ARCSIX (Gulfstream III - LaRC)